
SAP VMS (Vehicle Management System) is an industry-specific solution within SAP (mainly for automotive and heavy equipment sectors) that helps companies manage the entire lifecycle of a vehicle — from procurement, production, sales, delivery, to after-sales services.
It works as an extension of SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) and SAP MM (Materials Management), focusing on vehicles as “products with unique configurations” rather than just generic materials.
For example:
Car manufacturers (like BMW, Tata Motors)
Dealers/distributors (like Toyota dealers)
Leasing and rental companies
They all use SAP VMS to track vehicles, options, customizations, pricing, and availability in real-time.
End-to-End Vehicle Tracking
Tracks vehicles from production to final sale.
Transparency of vehicle status across manufacturing, logistics, and dealers.
Configuration & Customization
Manages different configurations (color, model, add-ons, engine type).
Reduces errors in ordering customized vehicles.
Integration with SAP Modules
Works seamlessly with SAP SD, MM, FI, CRM, and Logistics.
Streamlines order-to-delivery processes.
Inventory Optimization
Real-time vehicle stock visibility at plants, dealers, and warehouses.
Helps avoid overstocking or shortages.
Faster Sales & Delivery Process
Dealers can reserve, allocate, and sell vehicles more quickly.
Improves customer satisfaction.
Financial Control
Integrates with SAP FI/CO for vehicle costing, invoicing, and profitability analysis.
Compliance & Reporting
Maintains regulatory compliance (tax, insurance, road permits, etc.).
Generates reports for management decisions.
Vehicle Lifecycle Management → Track from production order to customer handover.
Sales Process Automation → Streamline dealer orders, reservations, pricing, and discounts.
Customization Handling → Manage customer-specific vehicle variants (color, accessories, engine type).
Dealer & Distributor Network Integration → Syncs manufacturer, distributor, and dealer operations.
After-Sales Service → Facilitates warranty, repairs, recalls, and maintenance tracking.
Profitability & Analytics → Understand which models/configurations sell more profitably.
SAP VMS is designed for the automotive industry to streamline the complex supply chain, sales, and after-sales processes of vehicles. It ensures transparency, efficiency, and customer satisfaction across the vehicle’s entire journey.
| Aspect | Standard SAP SD/MM | SAP VMS (Vehicle Management System) |
|---|---|---|
| Product Type Handling | Handles generic materials (e.g., “Car Model X”). Doesn’t track unique vehicle IDs. | Handles vehicles as unique objects with Vehicle Identification Numbers (VINs), engine numbers, chassis numbers, and configurations. |
| Configuration & Variants | Limited capability – uses configurable materials (VC – Variant Configuration), but not designed for vehicle-specific options. | Specially designed for automotive customization (color, accessories, engine, insurance, financing options). Tracks every option per vehicle. |
| Lifecycle Tracking | Can track sales orders and deliveries, but not the entire lifecycle. | Full vehicle lifecycle management – from production order → shipment → dealer → customer → after-sales. |
| Inventory Management | Tracks stock at material level only. | Tracks stock at vehicle level – each car/truck tracked individually in the pipeline (factory, port, dealer stock). |
| Sales & Reservation | Standard order-to-cash flow, but no dedicated vehicle allocation process. | Vehicle Reservation, Allocation, and Release features ensure correct car is matched to customer demand. |
| Dealer/Distributor Integration | Standard SD supports customers as business partners but doesn’t specialize in dealer networks. | Designed for dealer/distributor networks → manages ordering, allocation, stock visibility, and transfer between dealers. |
| Pricing & Financing | Standard pricing (condition techniques). Limited for automotive financing, insurance, or leasing models. | Built-in support for automotive pricing scenarios → includes financing, insurance, extended warranty, trade-in vehicles, etc. |
| After-Sales / Warranty | Needs SAP CS (Customer Service) or CRM for detailed warranty/service tracking. | Directly integrates with warranty, recalls, and after-sales service processes tied to vehicle history. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Needs customization for vehicle-specific compliance (tax, road permits, registration). | Ready framework for automotive compliance (registration papers, road permits, insurance docs). |
| Analytics & Reporting | General sales/inventory reports, not specific to vehicles. | Vehicle-specific reports: stock aging, dealer allocation, sales trends, model profitability, pipeline tracking. |
Why Companies Adopt VMS Instead of Just SD/MM?
Unique Vehicle Tracking → VIN-level tracking is critical in automotive; SD/MM can’t handle this natively.
Customization Management → Automotive customers demand model/color/feature customization, which SD/MM struggles with.
Dealer Network Support → Automotive distribution is dealer-driven; VMS is built with this in mind.
Lifecycle Transparency → From factory → port → dealer → retail → after-sales, all managed in one system.
Customer Experience → Faster reservations, fewer errors, transparency on delivery timelines.
Integration with Finance/Leasing → Automotive often involves loans, leasing, or insurance; VMS handles these.
Standard SAP SD/MM = Good for general products (fast-moving goods, retail, manufacturing, etc.)
SAP VMS = Tailor-made for automotive (vehicles are unique, configurable, regulated, and expensive).
Example: Selling a Car
Standard SAP SD/MM
The manufacturer creates a material (“Car Model X”) in SAP MM.
Production order is processed, and stock is updated at the material level.
No unique VIN/chassis/engine tracking unless heavily customised.
SAP VMS
Each car is created as a unique vehicle object with a VIN (Vehicle Identification Number), engine number, chassis number, and configuration (colour, features, accessories).
Vehicle is placed in pipeline stock (production → shipment → dealer).
Standard SAP SD/MM
Dealer order is processed as a sales order in SAP SD.
Only the material code is considered (e.g., 20 units of Model X).
No visibility on which exact cars (VINs) are being allocated.
SAP VMS
The dealer creates a vehicle order in VMS.
Specific vehicles (with VINs, options, and colors) are reserved and allocated to the dealer.
Real-time visibility: dealer knows exactly which car (white sedan, VIN XYZ123, with sunroof) is coming.
Standard SAP SD/MM
Goods movement updates the stock at the dealer location.
Still tracked at the material level only (e.g., 5 cars of Model X).
SAP VMS
Stock updated at vehicle level → each VIN is tracked at the dealer.
The dealer knows exactly which cars are in stock (VIN A = Blue, VIN B = Black with leather seats).
Standard SAP SD/MM
The dealer creates a sales order/invoice.
A generic car is sold (Model X). If the customer requested a specific colour, it must be manually checked in stock.
No built-in system to track customer-specificcustomisationn.
SAP VMS
Dealer checks available vehicles in VMS (filtered by colour, variant, features).
Allocates a specific VIN to the customer.The systemm generates sales contracts, invoices, insurance details, and finance options.
Vehicle lifecycle record is updated → VIN XYZ123 now belongs to Customer ABC.
Standard SAP SD/MM
Needs SAP CS/CRM integration to manage warranty and service.
Warranty claims are generic (linked to the product, not the vehicle identification number, or VIN).
SAP VMS
Warranty and service history are directly linked to the VIN.
If there’s a recall, the company knows exactly which customers/dealers to contact (based on VIN).
Easy tracking of repairs, insurance, and maintenance.
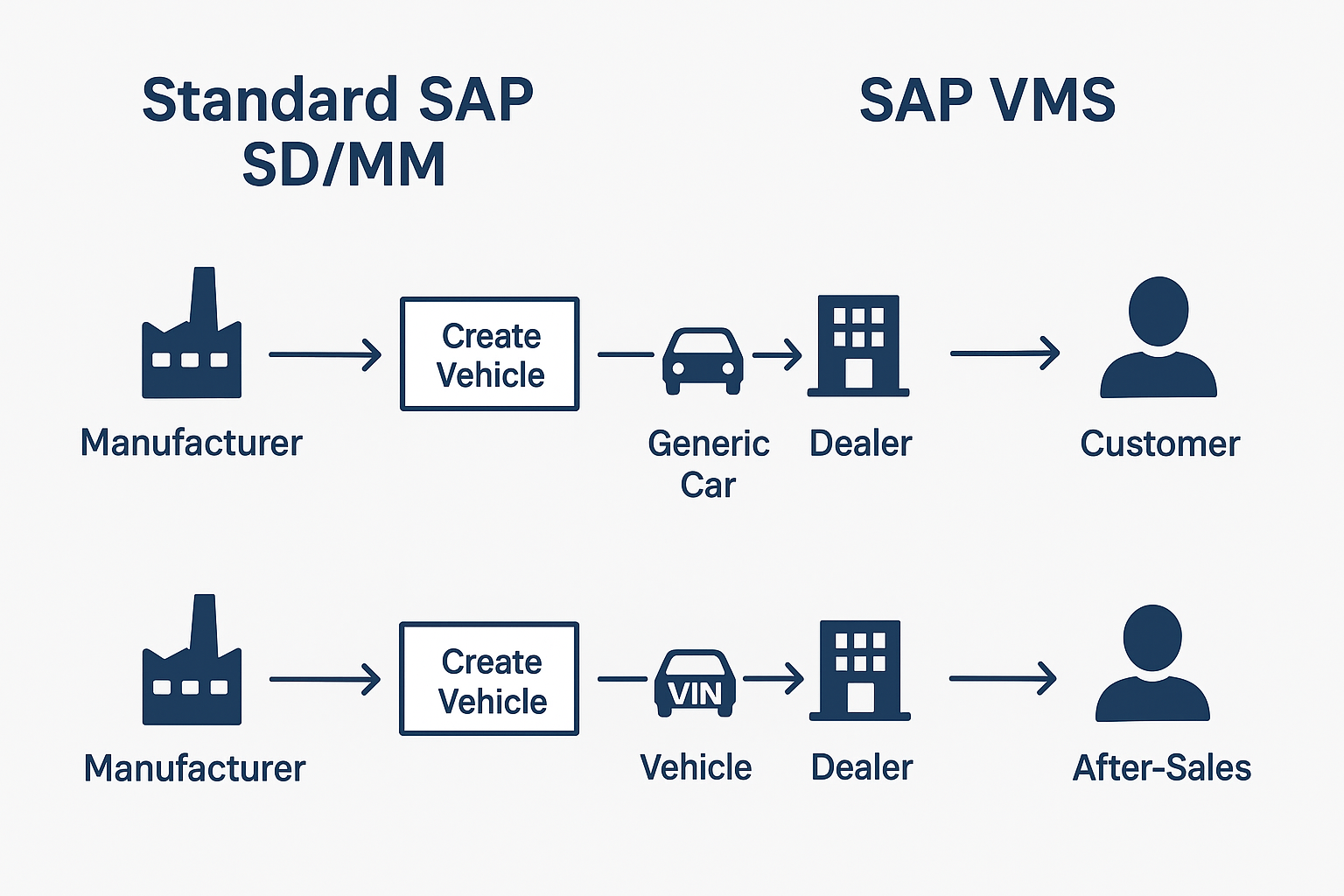
SD/MM → Treats cars like generic products (“Car Model X”), without unique identification.
VMS → Treats each car as a unique, configurable product (VIN-based) and supports dealer operations, customer-specific requirements, compliance, and after-sales.
That’s why automotive OEMs, importers, and dealers prefer SAP VMS:
It ensures end-to-end visibility, accurate customer delivery, and smoother dealer operations.
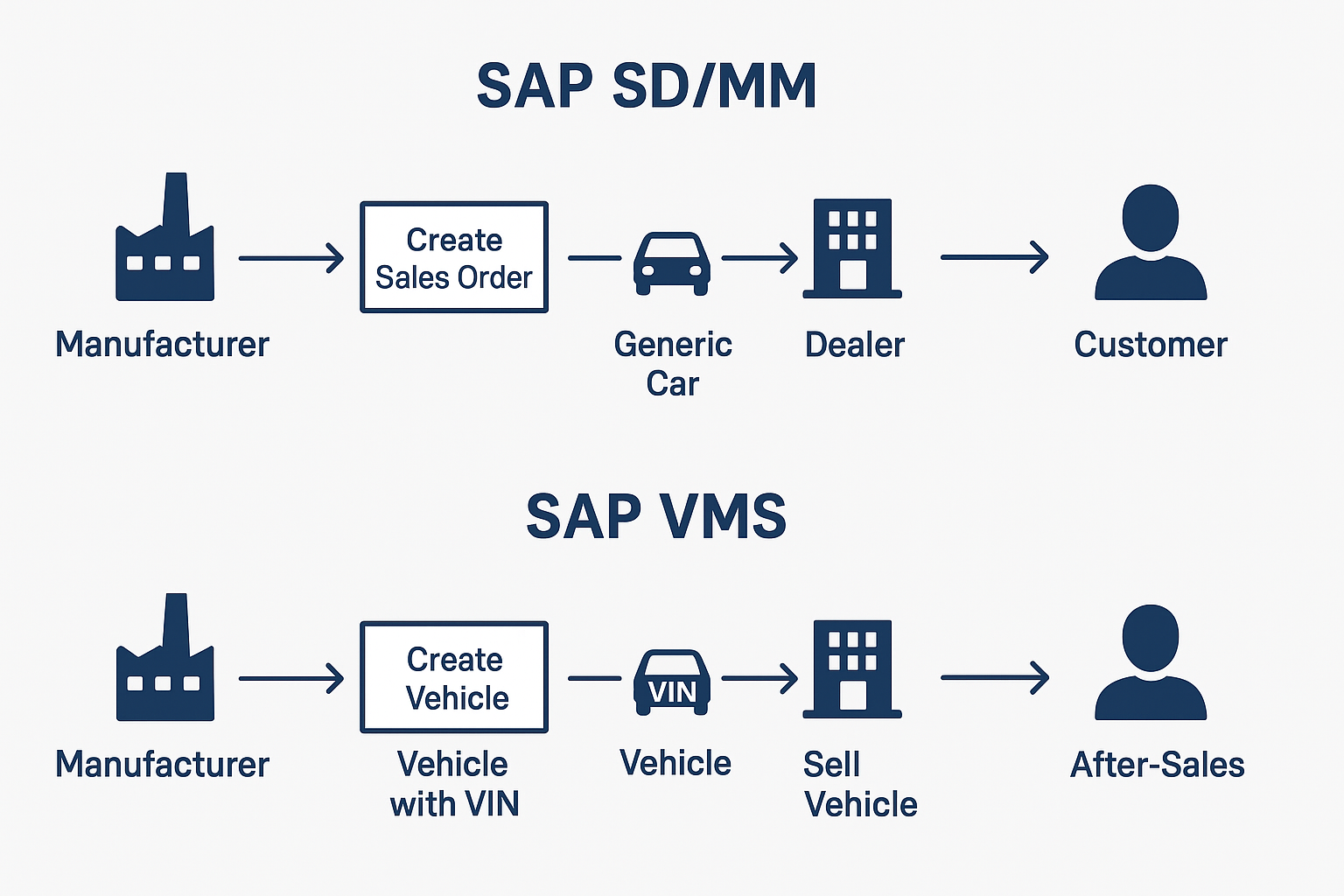
Here’s the visual flow diagram comparing SAP SD/MM vs SAP VMS in the vehicle lifecycle:
It shows how the same cycle (Manufacturer → Dealer → Customer → After-Sales) is handled differently in Standard SD/MM vs VMS.
